Commands which we use in mongoDB.
Create a database
use company // create a database
If it is already exist provide it, otherwise create it.
View all databases
show dbs
Database එකක් අලුතෙන් create කර මෙම command එක run කලද එම අලුත් database එකට document එකක් add වන තුරු එම database එක පෙන්වන්නේ නැත.
Drop a data base
db.dropDatabase() //Dropping a current woking database
Create a collection.
db.createCollection("branch")
db.branch.insert({"code":"001", "name":"branch one"})
// create a document. Inhere branch Collection also create and then document is created.
View Collections
show collections // show created collection
View Collection data
db.branch.find()
Drop a Collection
db.employee.drop() // remove collection
Adding Document.
මෙහෙදී Binary Jason Format හෙවත් BSON එක යොදා ගනු ලබයි.
Single record.
db.branch.insert({"code":"001", "name":"branch one"})
Multiple record.
db.branch.insert(
[
{"bId":"001", "bLocation":"Colombo","bTP":"b0771234567"},
{"bId":"002", "bLocation":"Kandy","bTP":"b0771235567"},
{"bId":"003", "bLocation":"Galle","bTP":"b0771230000"}
]
)
අපි Database එකට data insert කරන විට mongoDB වලින් ඒ ඒ record එකට default ම unique id එකක් generate කරගනු ලබයි.එම ID එක අපට provide කරනටද පුළුවන් වේ.
Finding data.
find() and fIndOne() සැලකිමේදී find() මගින් entire collection එකේම search කර අදාළ සියලුම document ලබා දෙන අතර, findOne() මගින් පලවෙනි එක හොයාගත්තම document එක return කිරීම කරයි.එම නිසා find() ට වඩා findOne() එක speed වේ.
db.employee.find()
db.employee.findOne()
db.employee.find({"code":"001"})
db.employee.findOne({"code":"001"})
// find one is more speed because it find 1st result and return it.Bu in find() it will find all the record in the entire collection.
db.employee.find({"salary":"23000"}) // equal
db.employee.find({"salary":{$ne :"23000"}}) // not equal
db.employee.find({"salary":{$gt :"23000"}}) // gt - breater than
db.employee.find({"salary":{$gte :"23000"}}) //gte - greater than or equal
db.employee.find({"salary":{$lt :"29000"}}) // lt - breater than
db.employee.find({"salary":{$lte :"29000"}}) //lte - greater than or equal
AND, OR conditions (SQL වලනම් && සහ ||).
//And
db.employee.find({"salary":"23000","age":45})
db.employee.find({"salary":{$gt :"20000"},"age":{$gt :35}})
//Or
db.employee.find({$or : [{"salary":"23000","age":45}]})
db.employee.find({$or : [{"salary":{$gt :"20000"},"age":{$gt :35}}]})
//both
db.employee.find({"age":{$lt :55},$or : [{"code":"002","salary":{$gt :"20000"}}]})
Updating
// updating
db.employee.update({"_id" : ObjectId("5f5ca367ccb1774f207b1dd7")},{$set:{"salary" : "28000"}})
db.employee.update({"age":{$lt :50}},{$set:{"salary" : "25000"}})//age එක 50 ට අඩු පළමු document එක විතරක් update කරයි.
db.employee.update({"age":{$lt :50}},{$set:{"salary" : "25000"}},{multi:true})// age එක 50 ට අඩු සියලුම document update කරයි.
db.employee.save({ "_id" : ObjectId("5f5ca367ccb1774f207b1dd7"), "code" : "002", "addrss" : "Main Steet,Kandy 04", "salary" : "25000", "age" : 36.0})
save වලදී id = "5f5ca367ccb1774f207b1dd7" search කරන අතර එහෙම එකක් තියනවනම් new valuess වලින් old එක update කරන අතර එහෙම එකක් නැත්තන් new document එකක් create කරනු ලබයි.
Removing Elements.
db.employee.remove()//කිසිම augment එකක් pass නොකරන්නේ නම් employee collection එකේ ඇති සියලුම documents remove කරනු ලබයි.
db.employee.remove({"_id" : ObjectId("5f5ca367ccb1774f207b1dd7")})
db.employee.remove({"age":45})// remove all documents, which age is = 45
db.employee.remove({"age":45},1)// even given condition find multiple documents, then delete one document only
Projection
Selecting only necessary data rather than selection the all data from a document.
// Syntax - db.COLLECTION.remove({},{KEY:1 OR 0})
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0})// first one should be empty {}. 1 - we want that data , 0 - we do not want that data
limit, skip and sort
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).limit(2) // employee collection එකෙන් document 2k පමණක් fetch කරන්න
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).skip(2) // employee collection එකෙන් document වල පළමු 2k අත්හැර ඉතුරු ටික පමණක් fetch කරන්න
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).limit(2).skip(1)
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).skip(1).limit(2) // Both are same.පළමුවෙනි document එක අතහැර ඊලග document දෙක ගන්න
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).sort({"salary":1}) // get document according acceding order of salary.[23000,290000,33000]
db.employee.find({},{"age":1,"_id":0,"code":1, "addrss":1,"salary":1}).sort({"salary":-1}) // get document according descending order of salary.[33000,290000,23000]
Indexing
Indexes are the special data structure that sores a small portion of data set to easy to pass way. Mongo database is really large, it can have millions of records. If we want to find one document among those it is very important to use indexing.
Adding large amount of document to test the indexing.
for(i = 5; i<1000000;i++){
db.employee.insert(
{"code":"003"+i, "addrss":"Main Steet,Galle "+i,"salary":"33000","age":55}
)
}
Create index
db.employee.createIndex({"salary":1})
Fetch document
db.employee.find({"salary":"23000"})
Drop Index
db.employee.dropIndex({"salary":1})
MongoDB Aggregation
This groups values from multiple documents together and can perform variety of operations on that grouped data.it is going to return single result after the aggregation.
In the SQL we query select count and in the bracket Astrix this count for aggregation. It return the number of rows. This is same in mongoDB.
db.employee.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$gender", genderCount: { $sum: 1 } } }
]) // $sum: 1 :1 - true
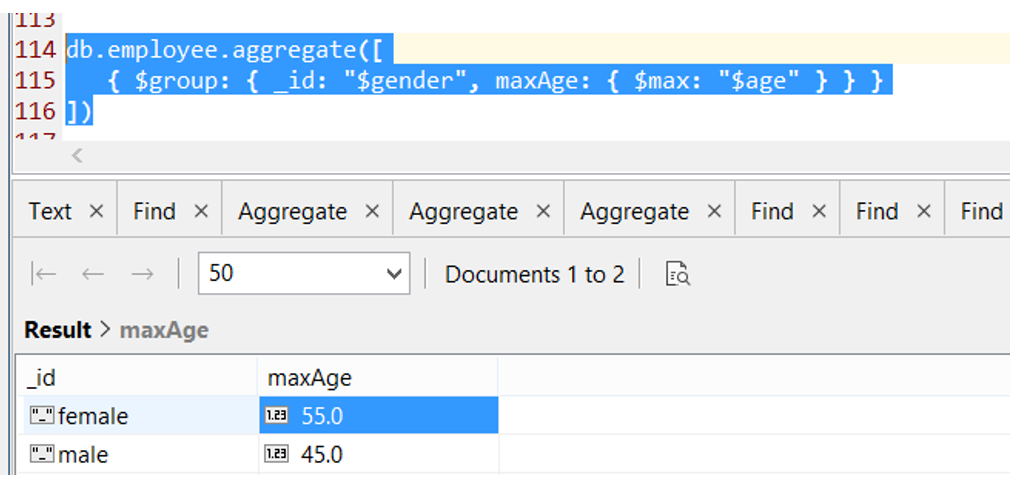
db.employee.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$gender", maxAge: { $max: "$age" } } }
])
Bellow example is from https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/aggregation/
Single Purpose Aggregation Operations
db.employee.estimatedDocumentCount()
db.employee.count()
db.employee.distinct("salary")
MongoDB Backup and Restore
Backup
Open lib location (C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.6\bin) in CMD administrative mode
To back up all the databases
Run mongodump in CMD.
To back up a specific databases
Run mogodump --db databasename in CMD.
Example: mogodump --db company
To back up a specific collection.
Run mogodump --db databasename --collection collectionname in CMD.
Example: mogodump --db company --collection employee
Restore
Open lib location (C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.6\bin) in CMD administrative mode
To restore all the databases
Run mongorestore in CMD.
To restore a specific databases
Run mongorestore --db databasename dump/databasename in CMD.
Example: mongorestore --db company dump/company
To restore a specific collection
Run mongorestore --db databasename --collection collectionname in CMD.
Example: mongorestore --db company --collection employee dump/employee/employee.bson








Comments
Post a Comment