01. Spring – Introduction ,Architecture.
SPRING MVC
Web
application වලදී මුලිකව වෙන්නේ clients requests කරනවා.ඒවා
identify කරගෙන response
දෙනවා.Java
වලදී client
එවන request
එකකට response
කරන්නේ servlet
එකක් කියන java
class එකක්.මෙහිදී වන process
එක මෙහෙමයි,
එවන සෑම request
එකක්ම web.xml
file එකෙන් catch
කරගන්වා.ඒ request
එකට response
කරන servlet
එක පිළිබද details
ටික එකේ configure
කරලා තියෙන්නේ.ඒ හරහා එම request එක එම servlet එකට යවලා response
එක දෙනවා. එක servlet
එකකට පුළුවන් එක request එකකට response කරන්න විතරයි.එම නිසා request
එකෙන් request
එකට servlet
හදන්න ඕනේ සහ එම
servlet පිළිබද විස්තර web.xml
එකේ කරන්න configure
ඕනේ.
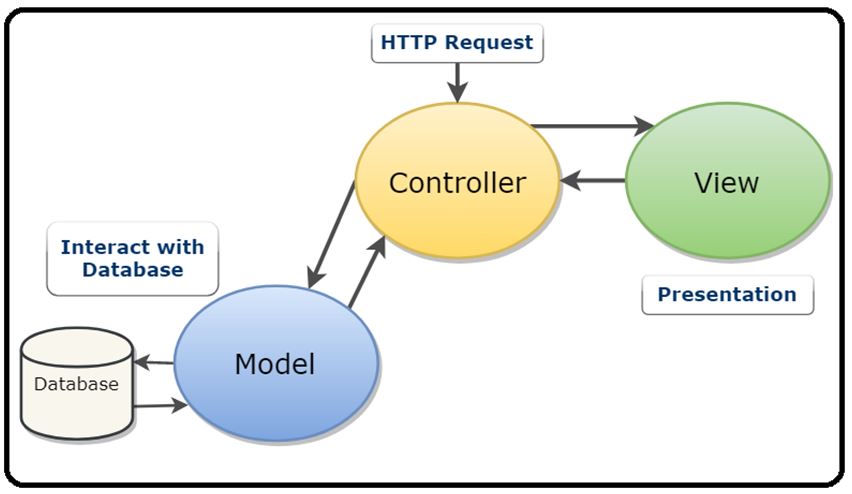
MVC (Model View Controller)
ඕනෑම web application එකක view
part එකක් සහ එම views
වලට අදාළ data
process කරන back
end part එකක් තියනවා.view කියන්නේ එක part එකක්,data(model) කියනේ තව part
එකක්.මේ part
දෙක මානව control
කරමින් model
සහ view
අතර properly
data manage කරන්න අතරමැදියක් ලෙස controllers බාවිතා
කරනවා.
SPRING
MVC වලදී වෙන්නේ මෙහෙමයි, එවන සෑම
request එකක්ම web.xml
catch කරනවා. Request
එකෙන් request
එකකට වෙන වෙනම servlet වලට map වෙන්නේ
නෑ. ඒ සෑම request එකක්ම යවන්නේ එක servlet එකකට.එම servlet
එකට dispatcher
servlet එක කියලා කියනවා.මෙය Spring
වලින් provide
කරන servlet
එකක් වෙනවා. ඒ dispatcher
servlet ගැන කරන්න ඕනේ configuration
ටික web.xml
හි ලියන්න ඕනේ.තවද dispatcher servlet කියන spring වලින් provide කරන class එක සමගද configurations
කරන්න ඕනේ. එම configurations
වලට application
context කියලා වෙනම xml
fileඑකක් generate
කරන්න ඕනේ(සමහරවිට front controller
කියලද කියනු ලබයි).මෙම xml
එක බාවිතයෙන් තමා ඒ ඒ request වලට අදාලව map වෙන්න
ඕන controllers මොනාද(servlet
නෙවෙයි),render
වෙන්න ඕනේ views
පිළිබද details
වගේ ඒවා configure
කරන්නේ.
Spring ව්ලදී Controllers තමා request වලට response කරන්න බාවිතා කරන්නේ. Servlet එකට වාඩා මෙහි ඇති විශේෂත්වය තමයි එක controller එකකට request කීපයකට response කල හැකි විම. එනම් controller class එක තුල වනුයේ ඒ ඒ request වලට response කරන්න method define කරීමයි.තවද එක spring application එකක controllers එකක් හෝ කීපයක් තිබෙන්නට ද පුළුවන්.
මෙය
පහසුවෙන් තේරුම් ගැනීමට පහත diagram
එක බලන්න.
Controllers
කලින් servlet ගොඩක් use කළා requests
වලට response
කරන්න.දැන් තියෙන්නේ controller ගොඩක්
වන අතර එක controller
එකකට request
URL එකකට වඩා තිබිය හැක.එනම් request වැඩි ගානකට response කල හැක.
Example.
එක controller එකකට request
5 කට response
කරන්න පුළුවන් ලෙස code කර ඇත. Front controller එකේ configure
කරනවා මෙම controller
එක මොන URL
වලටද response
කරන්නේ කියලා.එන URL
pattern එක අනුව එන request
එක අදාළ controller
එකට delegate
කරනවා.ඊට පස්සේ controller
එක කරන්න ඕනේ වැඩ ටික කරලා model එකක් generate කරලා (Model
or ModelAndView
object) front
controller ට එවන අතර
මොකද්ද view වෙන්න ඕනේ page
එක කියලත් front
controller ට කියනවා. Front
controller එකෙන් එම model
එක view
resolver (spring provide කරන class
එකකි) එකකට යවලා render
කරගෙන එම page
එක front
controller විසින් client
ට යවනවා.මේ ඔක්කොම වෙන්න servlet
engine එකක් තියෙන්න ඕනේ.එම නිසා මේ ඔක්කොම වෙන්නේ Tomcat, JBOSS වගේ servlet
engine එකක් ඇතුලේ.
web.xml
<web-app id = "WebApp_ID" version = "2.4" xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <display-name>Spring MVC</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <Servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Dispatcher-servlet.xml (This file is used for
configurations of org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
)
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns: context = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package = "com.lhu.controllers" /><mvc:annotation-driven /><bean class = "org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name = "prefix" value = "/WEB-INF/jsp/" /><property name = "suffix" value = ".jsp" /></bean> </beans>
Controller
Class
package com.lhu.controllers;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; @Controller@RequestMapping("/home")public class HomeController {@RequestMapping("/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)public String login(HttpServletRequest req,Model m) { String name=req.getParameter("name"); m.addAttribute("message", name); return "login"; }@RequestMapping("/home",method = RequestMethod.POST)public String passParametersWithModelMap(ModelMap map) { map.addAttribute("welcomeMessage", "welcome"); map.addAttribute("message", "Baeldung"); return "home";}@RequestMapping("/about",method = RequestMethod.POST)public ModelAndView passParametersWithModelAndView() {ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("about"); modelAndView.addObject("message", "Baeldung"); return modelAndView;}}
How
to get the rendering page.
Controller
එකට data
යැවීමට පහත ක්රම බාවිතා කරයි.
01.
PathVariable(http://localhost:8080/api/foos/1)
02.
RequestParam(http://localhost:8080/api/foos?id=abc)
Path variable
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)@GetMapping(value = "/user/{name}/{email}")public void process2(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String email) { logger.info("User name: {} and email: {}", name, email);} @ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)@GetMapping(value = "/book/{author}/{title}")public void process3(@PathVariable Map<String, String> vals) { logger.info("{}: {}", vals.get("author"), vals.get("title")); }
Request Param
//http://localhost:8080/api/foos?id=abc@GetMapping ("/api/foos")@ResponseBodypublic String getFoos(@RequestParam String id,@RequestParam(value=”id”) String myId) { return "ID: " + id;} @PostMapping ("/api/foos")@ResponseBodypublic String addFoo(@RequestParam(name = "id") String fooId, @RequestParam String name) { return "ID: " + fooId + " Name: " + name;} Method parameters annotated with @RequestParam are required by default. This means that if the parameter isn’t present in the request, we'll get an error:400 Bad RequestRequired String parameter 'id' is not presentWe can configure our @RequestParam to be optional, though, with the required attribute://http://localhost:8080/api/foos?id=abc ID: abc//http://localhost:8080/api/foosID: null@GetMapping("/api/foos")@ResponseBodypublic String getFoos(@RequestParam(required = false) String id) { return "ID: " + id;}A single @RequestParam can have multiple values://http://localhost:8080/api/foos ID: test@GetMapping("/api/foos")@ResponseBodypublic String getFoos(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "test") String id) { return "ID: " + id;} //http://localhost:8080/api/foos?id=1,2,3 IDs are [1,2,3]//http://localhost:8080/api/foos?id=1&id=2 IDs are [1,2]@GetMapping("/api/foos")@ResponseBodypublic String getFoos(@RequestParam List<String> id) { return "IDs are " + id;}






Comments
Post a Comment